What Is Electrical Current? Simple Explanation for Beginners (Water Hose Analogy)
- PLC Play Ground
- 0
- Posted on
What Is Electrical Current? Simple Explanation for Beginners
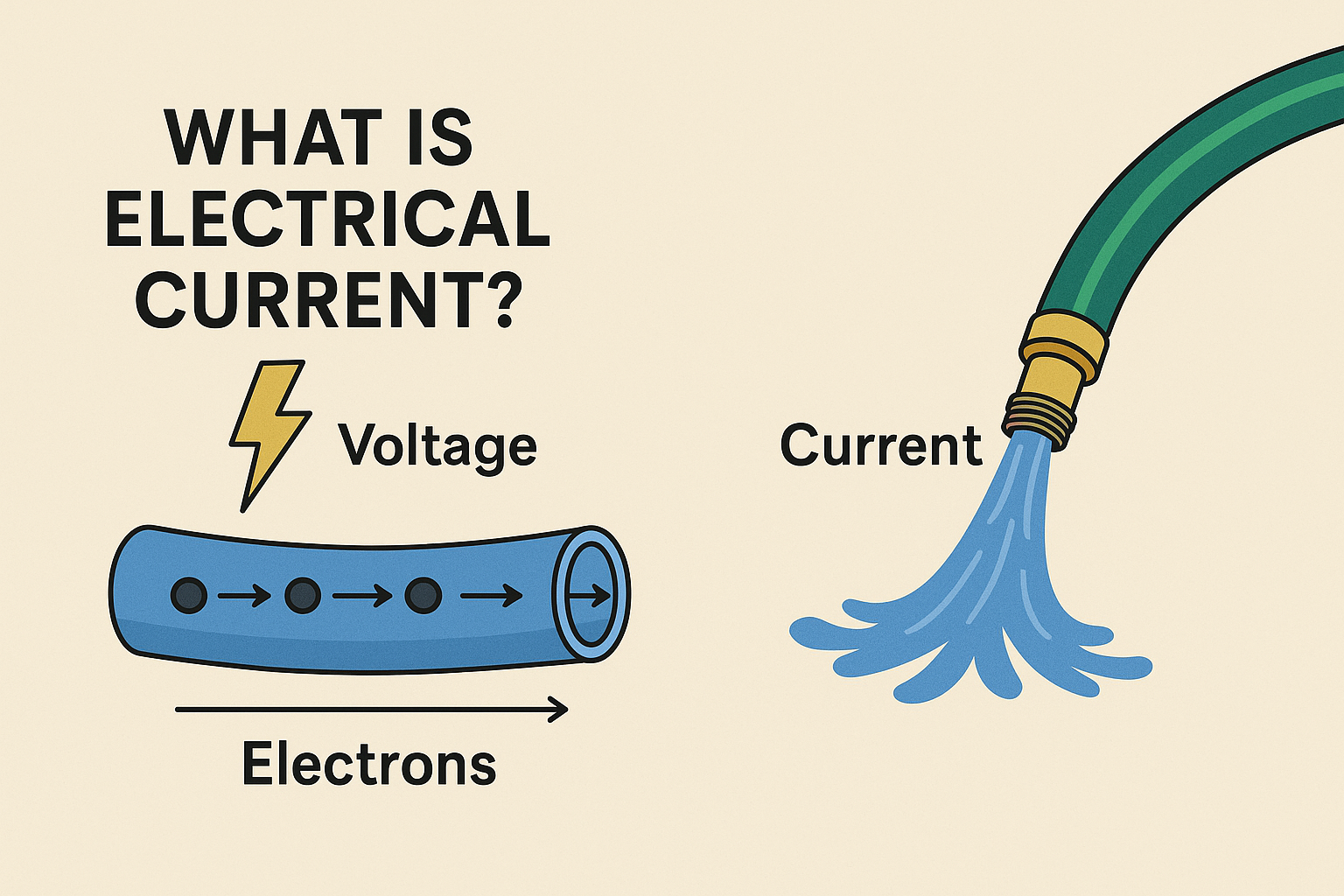
If you’ve already learned that voltage is the push, then electrical current is the actual flow of electrons moving through a wire.
This beginner-friendly guide uses simple analogies so anyone — even a 15-year-old — can understand it clearly.
Electrical Current Explained in the Easiest Way
Let’s return to the classic garden hose analogy:
- Voltage = pressure
- Current = how much water is flowing
More water flowing = higher current
More electrons flowing = higher current
Electrical current is measured in amperes (A) — often just called amps.
Explained for a 15-Year-Old
Imagine a busy school hallway:
- Students = electrons
- Hallway = wire
- How many students walk through per second = current
A packed hallway? High current
A nearly empty hallway? Low current
Even if the teachers (voltage) are pushing everyone forward, if there are only a few students, the flow (current) stays low.
This shows that current depends on two things:
1. Voltage (the push)
2. Resistance (how hard it is to move through the hallway)
Why Electrical Current Matters
Current tells you how much electricity is actually flowing through a device or wire.
Here’s why that’s important:
⚠️ Too much current
- Wires overheat
- Components can burn out
- Fires can occur if protection is missing
⚡ Too little current
- Devices don’t work properly or won’t power on
Examples:
- A phone charger provides only 1–2 amps
- A microwave uses 10–15 amps
- Big appliances need thick cables because high current creates heat
Real-Life Example: Wire Thickness
High-current devices use thicker wires because:
- Thick wire = lower resistance
- Lower resistance = less heat
- Safer for high current flow
That’s why extension cords for heaters, ovens, or power tools are heavier and thicker.
1-Minute Test: Check Your Understanding
- Current is the flow of ______.
a) voltage
b) electrons ✔️
c) power - Current is measured in:
a) watts
b) volts
c) amperes ✔️ - What happens if current is too high for a wire?
a) it cools down
b) it overheats ✔️
c) nothing - True or false: current can flow without voltage pushing it.
False ✔️ - Which device uses more current?
a) phone charger
b) microwave ✔️
Final Thoughts
Understanding electrical current helps you see why different devices need different cables, chargers, and safety limits.
Once you grasp current and voltage, almost every concept in electronics becomes much easier.
Want another beginner-friendly explanation? ⚡
Just ask!
