Tag: industrial automation
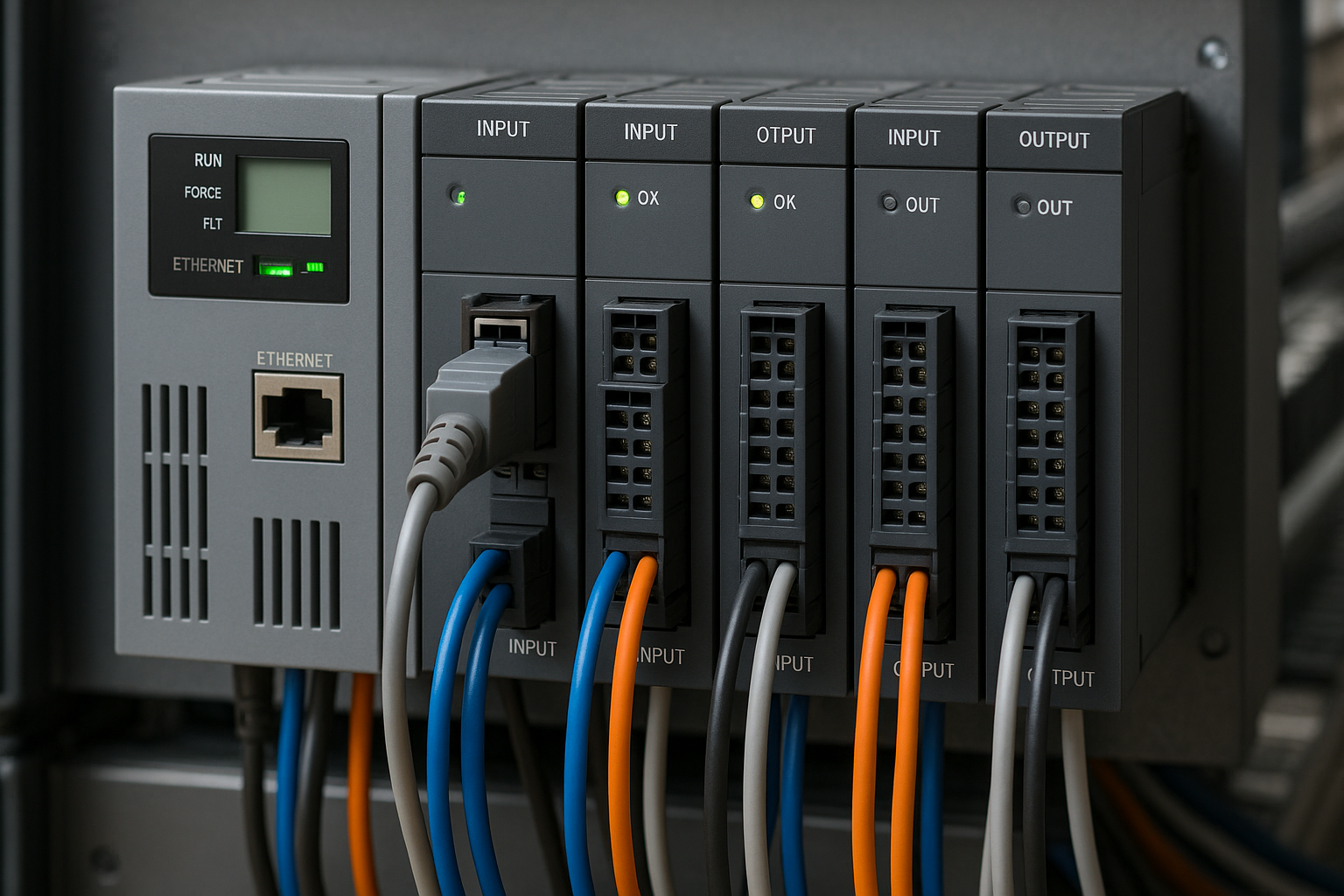

10 Common Uses of PLCs in Industry Today (With Examples)
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) are the backbone of modern industrial automation. Originally designed to replace relay logic, PLCs have evolved into powerful, flexible controllers capable of managing complex processes with high reliability. Today, they are used across virtually every sector that relies on machinery, production lines, or automated systems. Below are 10 of the most…
Read More
Servo Motor Encoders: A Simple and Clear Guide
Servo systems are everywhere in modern automation — from CNC machines and robotics to packaging equipment and conveyor systems. At the heart of every precise servo motor is one essential component: the encoder. In this easy-to-understand guide, we’ll explain what servo motor encoders are, why they matter, and how they work, without overwhelming technical jargon.…
Read More
Industrial Proximity Sensors: A Simple Guide for Beginners
In modern industrial automation, proximity sensors play a huge role in keeping machines smart, efficient, and safe. Even though they might look small, these sensors are responsible for detecting objects without touching them — a crucial ability in environments where precision and reliability matter. In this post, we will walk through what proximity sensors are,…
Read More
Analog Scaling: Converting 4–20 mA Signals Into Real-World Values
Many industrial sensors output a 4–20 mA signal, but your PLC can’t use that directly — it needs to convert the raw current into real-world units like °C, bar, or millimeters.This conversion process is called analog scaling, and getting it right is essential for accurate alarms, trends, and control logic. How Analog Scaling Works A…
Read More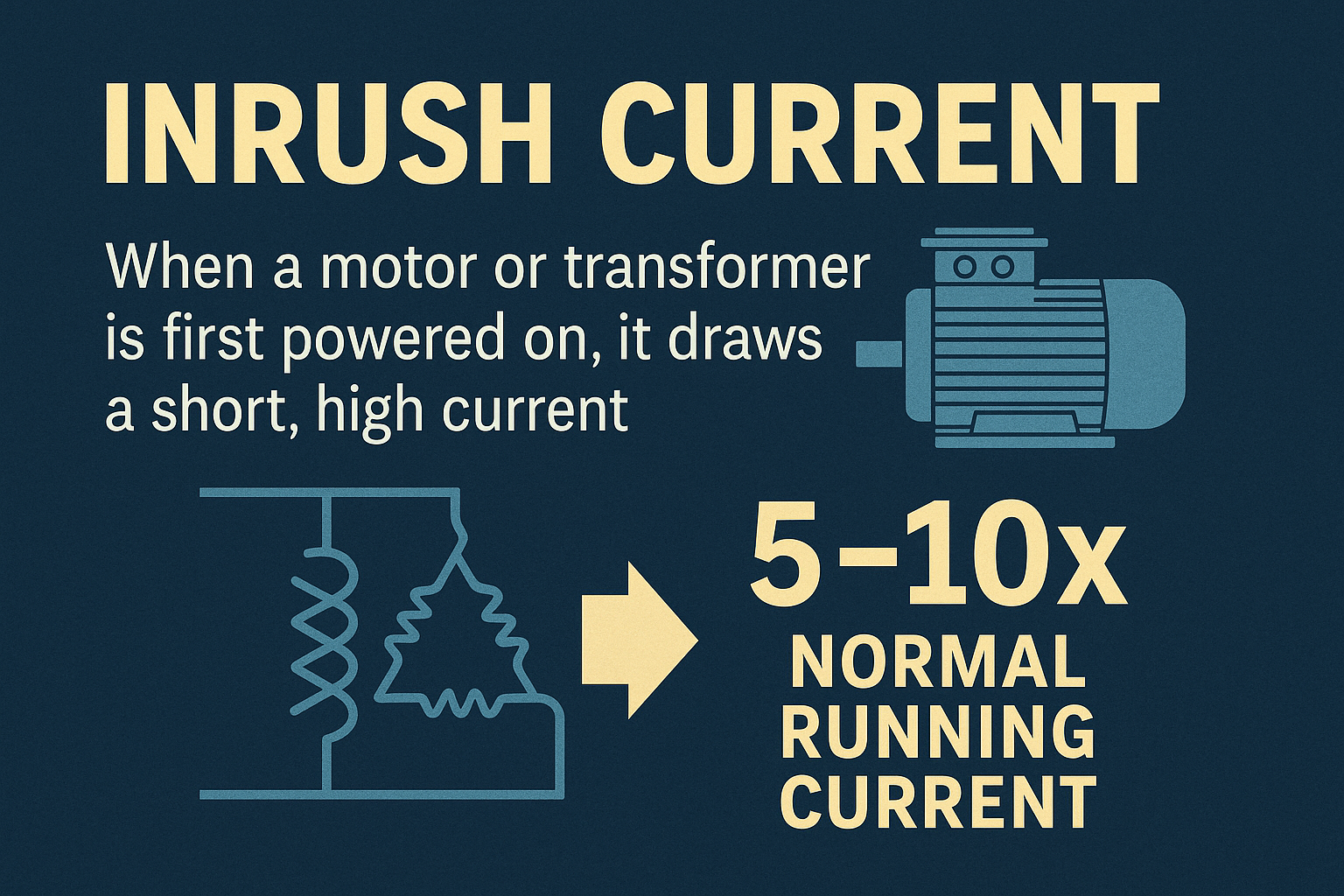
Understanding Inrush Current in Motors and Transformers
Understanding Inrush Current in Motors and Transformers When a motor or transformer first powers on, it draws a short but very high inrush current — often 5 to 10 times higher than its normal running current. This surge isn’t a fault. It happens because the device needs to magnetize its core or accelerate its load…
Read More