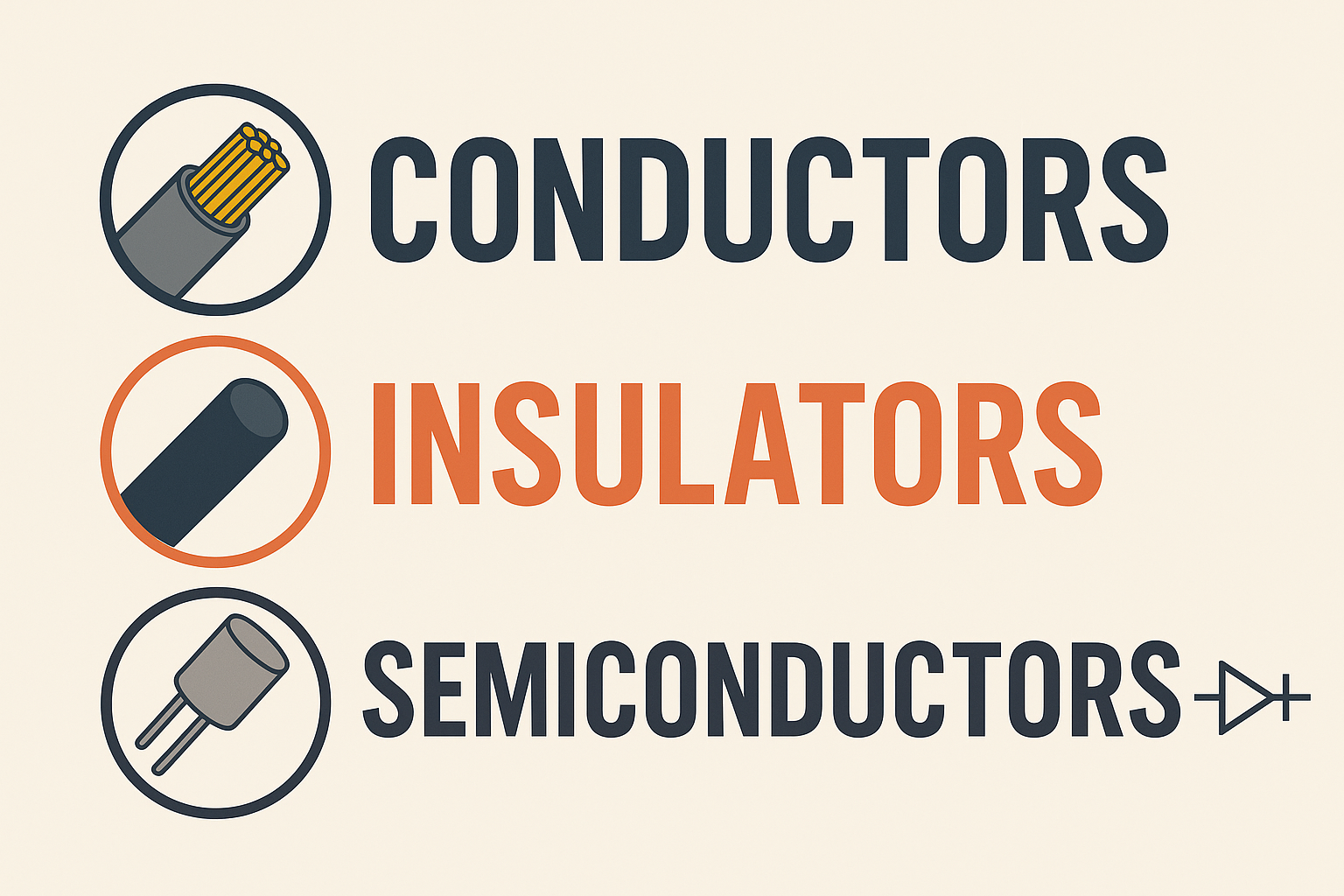
Conductors, Insulators, and Semiconductors: Electrical Basics Explained
- PLC Play Ground
- 0
- Posted on
Understanding how electricity moves through different materials is essential for anyone studying electronics or electrical systems. In this post, we’ll break down three major categories of materials: conductors, insulators, and semiconductors. Each plays a unique role in the world of electricity and modern technology.
What Are Conductors?
An electric current is created when free electrons can move from one atom to another.
Materials that allow many free electrons to move easily are known as conductors.
Common conductor materials include:
- Copper
- Silver
- Aluminum
- Zinc
- Brass
- Iron
Copper is the most widely used conductor because it balances performance and cost, making it ideal for wiring, motors, and countless electrical applications.
What Are Insulators?
Insulators are materials that do not allow free electrons to move easily.
Instead, they restrict electron flow, which makes them essential for electrical safety and containment.
Examples of insulators include:
- Plastic
- Rubber
- Glass
- Mica
- Ceramic
A typical electrical cable uses both conductors and insulators. The copper conductor inside carries the electrons, while the rubber or plastic insulation around it keeps those electrons safely contained and prevents accidental contact.
What Are Semiconductors?
Semiconductors are special materials—most commonly silicon—that have properties of both conductors and insulators. Their behavior changes depending on the external conditions applied to them.
When a semiconductor receives an external force (such as electrical voltage) in one direction, it may act like a conductor. When the force is applied in the opposite direction, it may act like an insulator.
This unique characteristic is the foundation of modern electronics. Semiconductor materials are used to create:
- Transistors
- Diodes
- Integrated circuits
- Most modern digital devices
Without semiconductors, today’s computers, smartphones, and microcontrollers simply wouldn’t exist.
Quick Review
Here’s a brief summary to reinforce the key points:
- Conductors: Allow many free electrons to flow.
- Insulators: Allow very few free electrons to flow.
- Semiconductors: Can act as either conductors or insulators depending on applied conditions.
Final Thoughts
Conductors, insulators, and semiconductors each play essential roles in electrical systems and modern electronics. Knowing how these materials work helps you understand everything from household wiring to the inner workings of microchips.
If you found this explanation helpful, feel free to explore more posts and continue learning about the fundamentals of electricity and electronics!
