Understanding Electron Theory: How Atoms Create Electricity
- PLC Play Ground
- 0
- Posted on
Electricity is something we use every day—when we turn on a light, charge a phone, or power a machine. But what is electricity at the most fundamental level? To answer that, we need to start with the smallest building blocks of matter: atoms.
In this article, we’ll explore electron theory, how electrons move, and how their movement becomes electrical energy.
What Is an Atom?
Everything around you—objects, liquids, gases, even living beings—is made of molecules.
Those molecules are made of atoms, and each atom has three main parts:
- Protons – positively charged
- Electrons – negatively charged
- Neutrons – neutral (no charge)
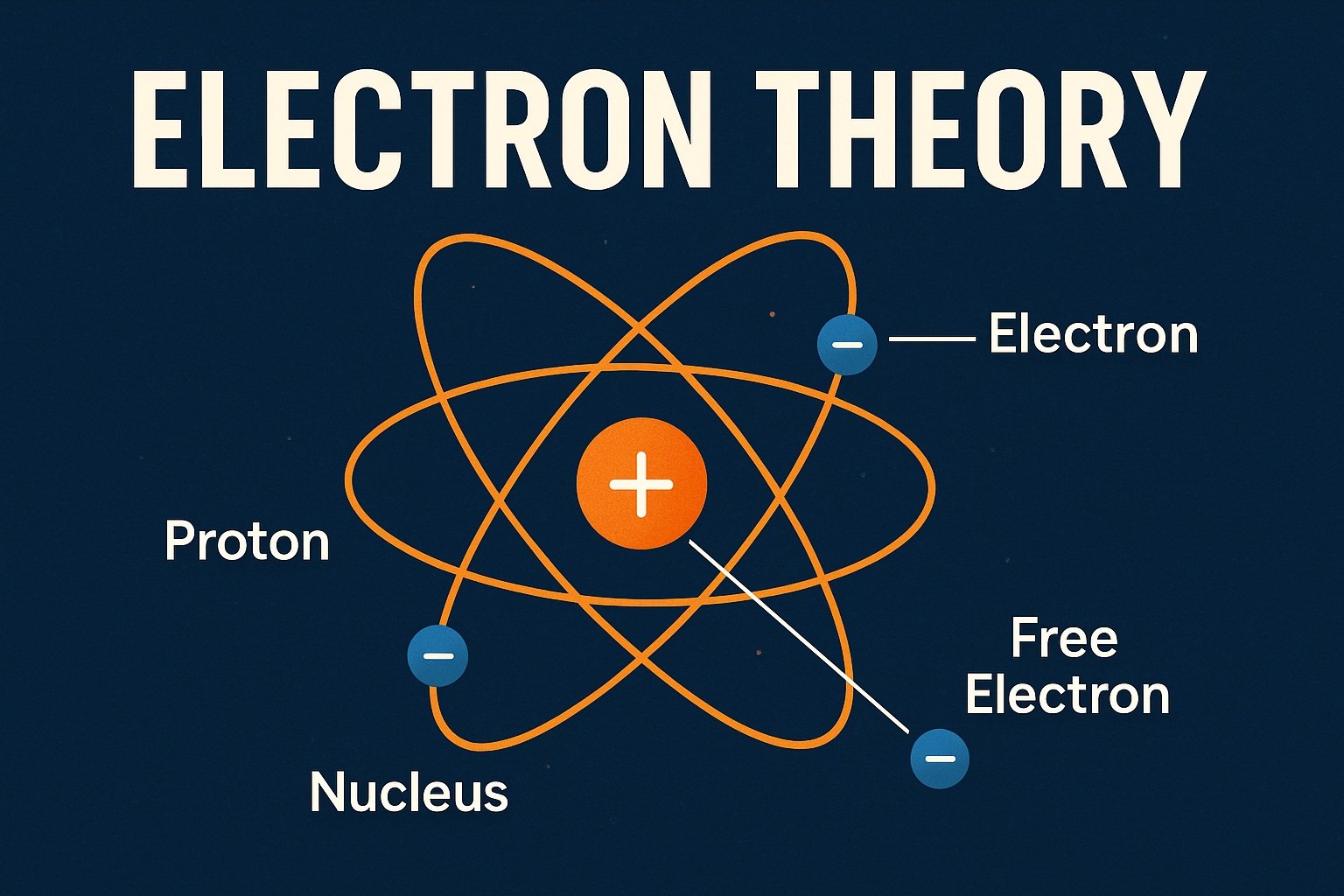
Protons and neutrons sit tightly packed in the nucleus, which forms the center of the atom.
Electrons orbit this nucleus, held in place by the attraction of the positively charged protons.
Most atoms contain an equal number of protons and electrons, keeping them electrically balanced.
Bound Electrons
The electrons that orbit close to the nucleus are tightly held by the proton’s attraction.
These are known as bound electrons. They stay in their orbit and do not move freely from one atom to another.
Free Electrons
Things get interesting in the outermost layer of the atom—the outer electron band.
Electrons in this outer layer are not held as tightly. With enough external force, they can break free.
These forces can include:
- Friction (like rubbing materials together)
- Movement through a magnetic field
- Chemical reactions
Once an electron is knocked loose, it becomes a free electron.
When a free electron leaves, it creates a “hole” that another electron can move into.
As electrons continue jumping from atom to atom, a chain reaction begins.
Electron Flow = Electricity
This movement of electrons from one atom to another is known as electron flow,
and electron flow is the fundamental basis of electricity.
Every electrical device you use—light bulbs, motors, computers—relies on the controlled flow of free electrons through wires and circuits.
Why Electron Theory Matters
Understanding electron theory helps explain:
- How electrical current is created
- Why some materials conduct electricity and others don’t
- How electrical circuits function
- The principles behind generators, batteries, and motors
It’s the foundation for all electrical engineering and electronics.
Final Thoughts
Electricity isn’t magic—it’s simply the movement of tiny particles called electrons.
By knowing how atoms and electrons behave, you gain a clearer understanding of how the electrical world around you really works.
If you enjoyed this explanation and want more simple lessons on electrical theory, feel free to explore more posts or leave a comment!
